一、简介 JDBC JDBC是java提供的连接数据库的规范。
JDBC连接数据库的步骤:
注册驱动和数据库信息
操作Connection,打开Statement对象
通过Statement执行SQL,返回结果到ResultSet中
使用ResultSet读取数据,通过代码转换为具体的POJO对象
关闭数据库。
ORM模型 操作数据库的过程复杂,ORM模型基于JDBC进行封装。ORM模型就是数据库的表和简单Java对象(Plain Ordinary Java Object,简称POJO)的映射关系模型 ,它主要解决数据库数据和POJO对象的相互映射。
Mybatis MyBatis是一个半自动映射的框架。之所以称它为半自动,是因为它需要手工匹配提供POJO、SQL和映射关系 。
二、Mybatis的构成 核心组件
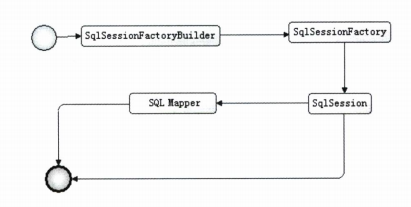
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(构造器):它会根据配置信息 或者代码来生成SqlSessionFactory (工厂接口)。SqlSessionFactory:依靠工厂来生成SqlSession(会话)。SqlSession:是一个既可以发送SQL去执行并返回结果 ,也可以获取 Mapper的接口。SQL Mapper:它是MyBaits 新设计的组件,它是由一个Java接口和XML文件(或注解)构成的 ,需要给出对应的SQL和映射规则。它负责发送SQL 去执行,并返回结果。
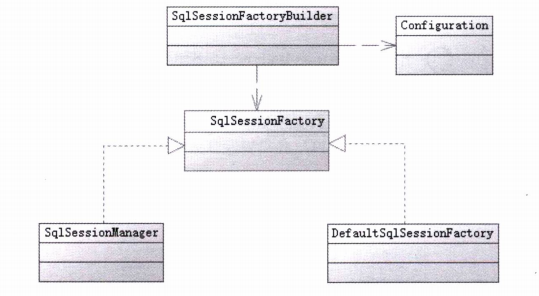
构建SqlSessionFactory 每个MyBatis 的应用都是以 SqlSessionFactory 的实例为中心的。SqlSessionFactory 的实例可以通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 获得。需要注意SqISessionFactory是一个工厂接口而不是现实类 ,它的任务是创建SqlSession。SqISession类似于一个JDBC 的Connection对象。MyBatis提供了两种模式去创建SqlSessionFactory:一种是XML 配置的方式,另一种是代码的方式。
Configuration的类全限定名为org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration,它在MyBatis 中将以一个Configuration类对象的形式存在,而这个对象将存在于整个MyBatis应用的生命期中 ,以便重复读取和运用。在内存中的数据是计算机系统中读取速度最快的,我们可以解析一次配置的XML文件保存到Configuration类对象中 ,方便我们从这个对象中读取配置信息,性能高。单例占用空间小,基本不占用存储空间,而且可以反复使用 。Configuration类对象保存着我们配置在 MyBatis的信息。在MyBatis中提供了两个SqlSessionFactory的实现类,DefaultSqISessionFactory和 SqISessionManager。不过SqlSessionManager目前还没有使用,MyBatis 中目前使用的是DefaultSqISessionFactory。
使用xml配置 配置一个XML,包含获取数据库连接实例的数据源(DataSource)、决定事务范围和控制方式的事务管理器(TransactionManager)和映射器(SQL Mapper)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd" > <configuration > <typeAliases > <typeAlias alias ="role" type ="com.learn.chapter2.po.Role" /> </typeAliases > <environments default ="development" > <environment id ="development" > <transactionManager type ="JDBC" /> <dataSource type ="POOLED" > <property name ="driver" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/number" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="123456" /> </dataSource > </environment > </environments > <mappers > <mapper resource ="mapper/AccountMapper.xml" /> </mappers > </configuration >
采用JDBC的事务管理模式
使用代码创建SqlSessionFactory
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class DatabaseInitialize private static final String config = "mybatis-config.xml" ; private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; private static DatabaseInitialize instance = new DatabaseInitialize(); private DatabaseInitialize () public DatabaseInitialize getInstance () return instance; } public void init () InputStream inputstream = null ; try { inputstream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream) ; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public synchronized SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory () return sqlSessionFactory; } }
创建SqlSession 在MyBatis 中 SqlSession接口的实现类有两个,分别是DefaultSqlSession和 SqlSessionManager。我们构建了SqlSessionFactory,然后生成 MyBatis 的门面接口 SqlSession。SqlSession接口类似于一个JDBC中的Connection接口对象 ,需要保证每次用完正常关闭它,所以正确的做法是把关闭SqlSession接口的代码写在 finally语句中保证每次都会关闭SqlSession,让连接资源归还给数据库。如果我们不及时关闭资源,数据库的连接资源将很快被耗尽,系统很快因为数据库资源的匮乏而瘫痪。让我们看看实现的伪代码,如代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 sqlsession sqlsession = null ; try { sqlsession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession (); sqlsession.commit(); }catch (Exception ex){ system.err.println (ex.getMessage ( )); sqlSession.rollback(); }finally { if (sqlSession != null ){ sqlsession.close(); } )
创建一个mapper文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.lq.mybatis.mapper.AccountMapper" > <resultMap id ="Account" type ="com.lq.mybatis.bean.Account" > <id property ="id" column ="id" > </id > <result property ="name" column ="name" > </result > <result property ="money" column ="money" > </result > </resultMap > <select id ="selectById" resultMap ="Account" > select id ,name ,money from account where id = #{id} </select > </mapper >
生命周期 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder SqlSessionFactoryBuilder是利用XML或者Java编码获得资源来构建SqISessionFactory的,通过它可以构建多个SessionFactory。它的作用就是一个构建器 ,一旦我们构建了SqlSessionFactory,它的作用就已经完结,失去了存在的意义。所以它的生命周期只存在于方法的局部 ,它的作用就是生成sqlSessionFactory对象。
SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory的作用是创建SqlSession ,而SqlSession就是一个会话,相当于JDBC中的Connection对象。每次应用程序需要访问数据库,我们就要通过SqlSessionFactory 创建SqISession,所以 SqlSessionFactory应该在MyBatis应用的整个生命周期中。而如果我们多次创建同一个数据库的SqlSessionFactory,则每次创建SqlSessionFactory 会打开更多的数据库连接(Connection)资源,那么连接资源就很快会被耗尽。因此SqlSessionFactory的责任是唯一的,它的责任就是创建SqlSession,所以我们果断采用单例模式 。
SqlSession SqlSession是一个会话 ,相当于JDBC的一个Connection对象,它的生命周期应该是在请求数据库处理事务的过程中 。它是一个线程不安全的对象 ,在涉及多线程的时候我们需要特别的当心,操作数据库需要注意其隔离级别,数据库锁等高级特性。此外,每次创建的SqlSession都必须及时关闭它,它长期存在就会使数据库连接池的活动资源减少,对系统性能的影响很大。它存活于一个应用的请求和操作 ,可以执行多条SQL,保证事务的一致性。
Mapper Mapper是一个接口,而没有任何实现类,它的作用是发送SQL ,然后返回我们需要的结果 ,或者执行SQL从而修改数据库的数据,因此它应该在一个 SqISession事务方法之内,是一个方法级别的东西 。它就如同JDBC中的一条SQL语句的执行,它最大的范围和SqlSession是相同的。
三、MyBatis的解析和运行原理 MyBatis 的运行分为两大部分,第一部分是读取配置文件缓存到Configuration对象,用以创建SqISessionFactory,第二部分是SqISession的执行过程。
构建SqlSessionFactory过程
通过org.apache.ibatis.builder.xm1.XMLConfigBuilder解析配置的XML文件,读出配置参数,并将读取的数据存入这个org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration类中。注意,MyBatis 几乎所有的配置都是存在这里的。
使用Confinguration对象去创建SqISessionFactory。MyBatis中的SqISessionFactory是一个接口,而不是实现类,为此 MyBatis 提供了一个默认的SqISessionFactory’实现类,我们一般都会使用它org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
这种创建的方式就是一种 Builder模式。对于复杂的对象而言,直接使用构造方法构建是有困难的 ,这会导致大量的逻辑放在构造方法中,由于对象的复杂性,在构建的时候,我们更希望一步步有秩序的来构建它,从而降低其复杂性 。这个时候使用一个参数类总领全局,例如,Configuration类,然后分步构建,例如,DefaultSqSessionFactory类,就可以构建一个复杂的对象,例如,SqlSessionFactory。
构建Configuration 在SqlSessionFactory构建中,Configuration是最重要的,它的作用如下。
读入配置文件 ,包括基础配置的XML文件和映射器的XML文件。初始化基础配置 ,比如 MyBatis 的别名等,一些重要的类对象,例如,插件、映射器、ObjectFactory 和typeHandler对象。提供单例 ,为后续创建SessionFactory 服务并提供配置的参数。执行一些重要的对象方法 ,初始化配置信息。
映射器的内部组成 映射器由3个部分构成
MappedStatement,它保存映射器的一个节点( select|insert|delete|update)。包括许多我们配置的SQL、SQL的id、缓存信息、resultMap、parameterType、resultType、languageDriver等重要配置内容。SqlSource,它是提供BoundSql对象的地方 ,它是MappedStatement的一个属性。BoundSql,它是建立SQL和参数的地方 。它有3个常用的属性:SQL、parameterObject、parameterMappings。
sqlSession运行过程 映射器的动态代理 Mapper映射是通过动态代理来实现的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class MapperProxyFactory <T > private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(); public MapperProxyFactory (Class<T> mapperInterface) this .mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface () return this .mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache () return this .methodCache; } protected T newInstance (MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this .mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this .mapperInterface}, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance (SqlSession sqlSession) MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this .mapperInterface, this .methodCache); return this .newInstance(mapperProxy); } }
这里可以看到动态代理对接口的绑定,它的作用是生成动态代理对象 ,代理的方法放入MapperProxy类中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class MapperProxy <T > implements InvocationHandler , Serializable private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L ; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy (SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) this .sqlSession = sqlSession; this .mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this .methodCache = methodCache; } public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this , args); } else { MapperMethod mapperMethod = this .cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(this .sqlSession, args); } } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod (Method method) MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this .methodCache.get(method); if (mapperMethod == null ) { mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this .mapperInterface, method, this .sqlSession.getConfiguration()); this .methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } }
Mybatis使用的是InvocationHandler,是一个JDK动态代理。上面运用了invoke方法。一旦mapper是一个代理对象,那么它就会运行到invoke方法里面 ,invoke首先判断它是否是一个类,显然这里Mapper是一个接口不是类,所以判定失败。那么就会生成MapperMethod对象,它是通过cachedMapperMethod方法对其初始化的,然后执行execute方法,把sqlSession和当前运行的参数传递进去。
MapperMethod采用命令模式 运行,根据上下文跳转,它可能跳转到许多方法中,我们不需要全部明白。我们可以看到里面的executeForMany方法,再看看它的实现,实际上它最后就是通过sqlSession对象去运行对象的SQL 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private <E> Object executeForMany (SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object param = this .method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); List result; if (this .method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = this .method.extractRowBounds(args); result = sqlSession.selectList(this .command.getName(), param, rowBounds); } else { result = sqlSession.selectList(this .command.getName(), param); } if (!this .method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) { return this .method.getReturnType().isArray() ? this .convertToArray(result) : this .convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result); } else { return result; } }
总结
Mybatis映射器的XML文件的命名空间对应的便是这个接口的全路径 ,那么它根据全路径和方法名便能够绑定起来,通过动态代理技术,让这个接口跑起来 。而后采用命令模式,最后还是使用SqlSession接口的方法使得它能够执行查询 ,有了这层封装我们便可以使用接口编程,这样编程就更简单了。
SqlSession的四大对象 Mapper执行的过程是通过 Executor、StatementHandler 、ParameterHandler 和 ResultHandler来完成数据库操作和结果返回的。
Executor 代表执行器,由它来调度 StatementHandler、ParameterHandler.ResultHandler等来执行对应的SQL。StatementHandler的作用是使用数据库的Statement (PreparedStatement)执行操作 ,它是四大对象的核心,起到承上启下的作用。ParameterHandler 用于SQL对参数的处理 。ResultHandler是进行最后数据集(ResultSet)的封装返回处理 的。
执行器(Executor) 执行器(Executor)起到了至关重要的作用。它是一个真正执行Java和数据库交互的东西。在 MyBatis中存在三种执行器。我们可以在 MyBatis 的配置文件中进行选择
SIMPLE,简易执行器,不配置它就是默认执行器。REUSE,是一种执行器重用预处理语句 。BATCH,执行器重用语句和批量更新 ,它是针对批量专用的执行器。
Configuration类中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public Executor newExecutor (Transaction transaction, ExecutorTypeexecutorType) executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;executorType =executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType. BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this , transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE ==executorType){ executor = new ReuseExecutor(this ,transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this , transaction) ; if (cacheEnabled){ executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
以SimpleExecutor为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor ... public <E> List<E> doQuery (MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null ; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this , ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } ... private Statement prepareStatement (StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } }
数据库会话器 数据库会话器(StatementHandler)就是专门处理数据库会话 的
Configuration类中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 public StatementHandler newStatementHandler (Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
RoutingStatementHandler不是我们真实的服务对象,它是通过适配模式找到对应的 StatementHandler 来执行的。在 MyBatis 中,StatementHandler和Executor一样分为三种:SimpleStatementHandler、PreparedStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler。
在初始化 RoutingStatementHandler对象的时候它会根据上下文环境决定创建哪个StatementHandler对象,我们看看RoutingStatementHandler 的源码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class RoutingStatementHandler implements StatementHandler private final StatementHandler delegate; public RoutingStatementHandler (Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break ; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break ; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break ; default : throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } } }
数据库会话器定义了一个对象的适配器delegate ,它是一个StatementHandler接口对象,构造方法根据配置来适配对应的StatementHandler对象 。它的作用是给实现类对象的使用提供一个统一、简易的使用适配器 。此为对象的适配模式,可以让我们使用现有的类和方法对外提供服务,也可以根据实际的需求对外屏蔽一些方法,甚至是加入新的服务 。PreparedStatementHandler为例,看看MyBatis是怎么执行查询的。执行器有三个主要的方法,prepare、parameterize和 query,
先看他们的父类BaseStatementHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler ... public Statement prepare (Connection connection) throws SQLException ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null ; try { statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } } protected abstract Statement instantiateStatement (Connection connection) throws SQLException }
instantiateStatement()方法是对SQL进行了预编译 。首先,做一些基础配置,比如超时,获取的最大行数等的设置。 然后,Executor 会调用parameterize()方法去设置参数。这个时候它是调用ParameterHandler去完成的,这里先看StatementHandler的查询方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler ... public <E> List<E> query (Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps); } public void parameterize (Statement statement) throws SQLException parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); } }
由于在执行前参数和SQL都被prepare()方法预编译,参数在parameterize()方法上已经进行了设置。所以到这里已经很简单了。我们只要执行SQL,然后返回结果就可以了 。执行之后我们看到了ResultSetHandler对结果的封装和返回 。
一条查询SQL的执行流程
Executor先调用StatementHandler 的 prepare()方法预编译SQL语句 ,同时设置一些基本运行的参数。
然后用parameterize()方法启用ParameterHandler 设置参数,完成预编译。
跟着就是执行查询,而update()也是这样的,最后如果需要查询,我们就用ResultSetHandler封装结果返回给调用者。
参数处理器 完成对预编译参数的设置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface ParameterHandler Object getParameterObject () ; void setParameters (PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException ;}
看实现类DefaultParameterHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public void setParameters (PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters" ).object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null ) { MetaObject metaObject = parameterObject == null ? null : configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); for (int i = 0 ; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null ) { value = null ; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { value = metaObject == null ? null : metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null ) jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1 , value, jdbcType); } } } }
是从parameterObject对象中取参数,然后使用typeHandler进行参数处理,如果你有设置typeHandler,那么它就会根据签名注册的typeHandler对参数进行处理。而typeHandler也是在 MyBatis初始化的时候,注册在Configuration里面的,我们需要的时候可以直接拿来用。这样就完成了参数的设置。
结果处理器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface ResultSetHandler <E> List<E> handleResultSets (Statement stmt) throws SQLException ; void handleOutputParameters (CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException }
DefaultResultSetHandler,在默认的情况下都是通过这个类进行处理的。这个实现有些复杂,它涉及使用JAVASSIST 或者CGLIB作为延迟加载 ,然后通过typeHandler和ObjectFactory进行组装结果再返回 ,因为我们需要改变它们的概率很小。
SqlSession运行总结 SqlSession是通过Executor创建StatementHandler来运行 的,而StatementHandler要经过下
prepared 预编译SQL。
parameterize设置参数。
query/update执行SQL。
其中parameterize是调用parameterHandler的方法去设置的,而参数是根据类型处理器.typeHandler去处理的。query/update 方法是通过resultHandler进行处理结果的封装,如果是update的语句,它就返回整数 ,否则它就通过typeHandler 处理结果类型 ,然后用 ObjectFactory提供的规则组装对象 ,返回给调用者。这便是SqlSession 执行的过程。